The pharmacovigilance trend is expected to become more prominent in the coming years.
In times of public health emergencies, pharmacovigilance and risk communication are essential.
In addition, machine learning techniques and access to large amounts of electronic healthcare data provide opportunities for improving the assessment of the drug benefit-risk profile in real-world settings.
Finally, innovative therapeutics have been marketed more frequently in recent years. Examples include medicines for advanced therapy, digital therapeutics, and vaccines created using advanced technologies. These medicines require special pharmacovigilance monitoring.
Pharmacovigilance is a critical aspect of the pharmaceutical industry that ensures drug safety and efficacy. It involves the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of adverse effects or other drug-related problems. As technology advances, pharmacovigilance faces both challenges and opportunities.
Challenges:
Big Data: One of the most significant challenges facing pharmacovigilance is big data management and analysis. With the increasing volume of data generated from electronic medical records, social media, and other sources, it becomes difficult to extract relevant information and identify potential safety issues.
Regulatory Changes: The regulatory landscape for pharmacovigilance is continually evolving, and keeping up with the changes can be challenging. Changes in regulations may require changes to data collection, reporting, and analysis methods, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
Globalization: The globalization of the pharmaceutical industry means that pharmacovigilance needs to be carried out across multiple jurisdictions, each with its own regulations and reporting requirements.
Adverse Events Reporting: Adverse event reporting is a vital part of pharmacovigilance, but it can be challenging to ensure accurate and complete reporting. Patients may not always report adverse events, and healthcare providers may not always recognize or report them.
Opportunities:
Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) can help in pharmacovigilance by analyzing large amounts of data quickly and accurately, detecting trends and patterns, and identifying potential safety issues.
Patient Engagement: Engaging patients in pharmacovigilance can improve adverse event reporting and increase patient safety. Patients can be educated on the importance of reporting adverse events and how to do it.
Digital Health: Digital health technologies such as wearable devices, mobile apps, and telemedicine can help with pharmacovigilance by monitoring patients in real-time and detecting adverse events early.
Real-World Data: The use of real-world data (RWD) can provide valuable insights into drug safety and effectiveness in real-world settings. RWD can complement clinical trial data and provide a more comprehensive understanding of a drug’s safety profile.
Future Trends and Major Constraints
Study participants are typically selected based on strict eligibility criteria, leading to difficulties when conducting studies. Adverse reactions may not be identified long-term in these patients because they are not representative of the actual population.
The post-marketing medicine evaluation process will make it easier to define the safety profile of any drug in a practical setting.
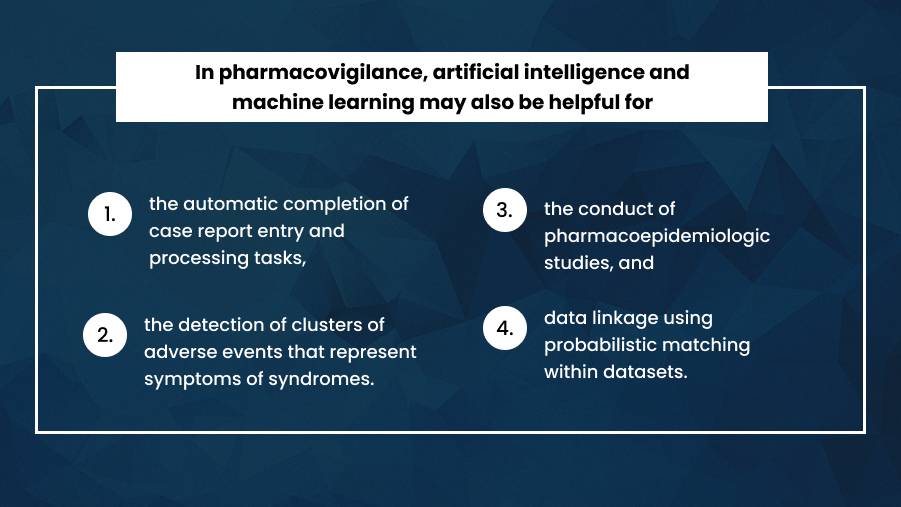
ML and AI may also improve pharmacovigilance by automating case report entries, identifying clusters of adverse events, and conducting pharmaco-epidemiological studies.
Using multiple models to predict negative outcomes and prevent them, as well as linking data using the probabilistic matching technique across datasets, are additional benefits.
With the right AI and ML techniques, many of the upcoming challenges relating to data from multiple sources, faster processing, and perhaps forecasting with accurate models may be resolved.
Conclusion
Pharmacovigilance is a critical component of the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring drug safety and efficacy. As technology advances, pharmacovigilance faces both challenges and opportunities. Artificial intelligence, patient engagement, digital health, and real-world data are some of the opportunities that can help overcome challenges and improve pharmacovigilance.
However, regulatory changes, big data, globalization, and adverse event reporting continue to be challenges that need to be addressed. By embracing cutting-edge technologies and adopting a patient-centric approach, pharmacovigilance can continue to evolve and improve patient safety.
Sollers College’s certificate program in pharmacovigilance aims to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of pharmacovigilance principles, processes, and regulations.
Students will also gain hands-on pharmacovigilance experience by participating in case studies, group discussions, and practical exercises.
The certificate program in pharmacovigilance at Sollers College is designed for individuals with a background in life sciences, pharmacy, or healthcare. Their goal is to develop their pharmacovigilance skills. The program is available online, and accessible to students worldwide.














