Why a career in Drug Safety & Pharmacovigilance may be an option for you?
Pharmacovigilance and Drug Safety is a thriving industry. In the coming years, regulatory authorities may make it mandatory for all small, medium, and large pharmaceutical companies to have a pharmacovigilance department. The Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance program is a worthwhile investment of time and energy for those with a foreign medical license attempting to establish a foothold in the country. Medical graduates are well-equipped in terms of knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding adverse drug reactions and their monitoring.
Opportunities for Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance Aspirants Abroad
The good news is that international medical graduates have a plethora of job opportunities in the United States. Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance is one career route that may offer the most potential for FMGs and anyone who wishes to make a mark in the medical enterprise.
It is one of the fastest-growing career categories in the country because of the increase in safety measures. The quick speed of change has also resulted in a genuine “skills gap,” The demand for well-paying Drug Safety associate employment vastly outnumbers the supply of skilled individuals.
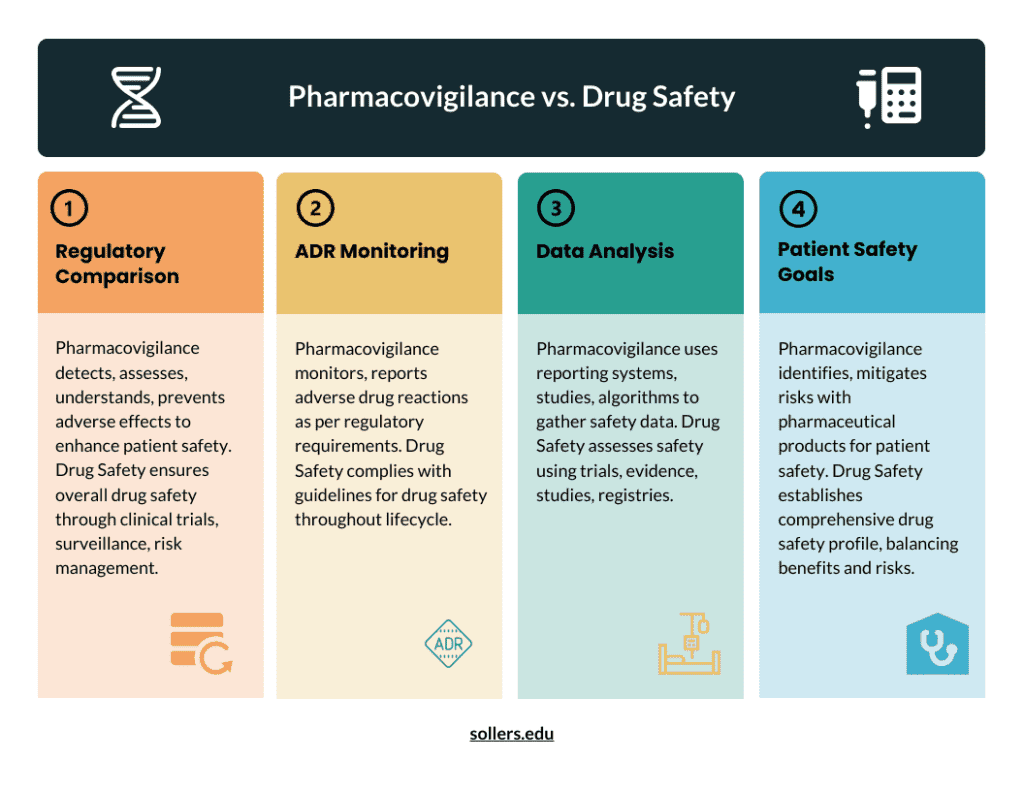
As a medical expert, you must address several challenges to assure the safety of medications and medical equipment. Medical practitioners must have a thorough awareness and competence in drug and device safety to effectively contribute to this goal by recognizing, managing, and reporting drug and device safety risks early on.
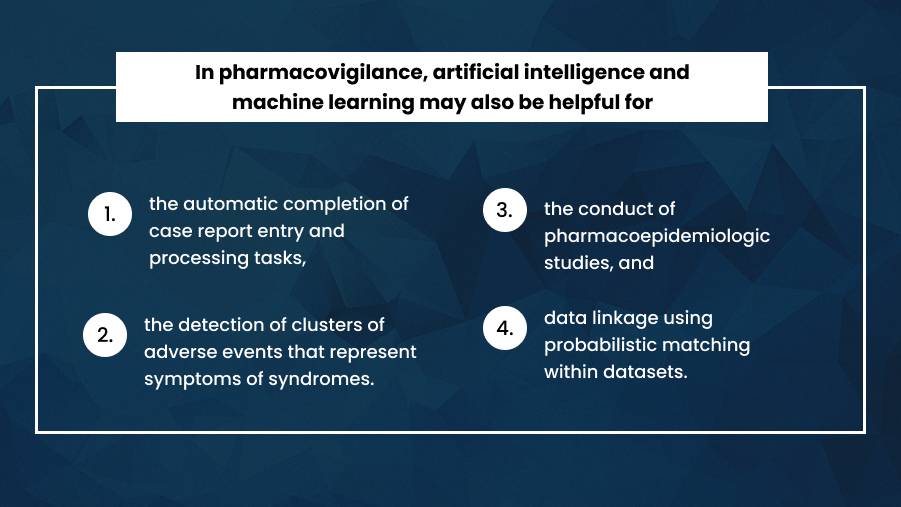
Pharmacovigilance has been increasingly important in recent years, and its relevance in the healthcare system is now well recognized. In the worldwide pharmacovigilance system, medical practitioners play a critical role. They demand a deep understanding and experience in drug and device safety and the ability to contribute to this field by identifying, managing, and reporting drug and device safety concerns early on. Medical practitioners should be officially trained in pharmacovigilance and have a mix of knowledge and abilities in this field.
There are various entry-level roles available for medical physicians, such as Drug Safety Physician, Medical Reviewer, and Safety Specialist / Scientist, all of which lead to higher positions over time.
People who love health care are in high demand. Employers in the health sector are looking for individuals with a unique blend of healthcare and information technology (IT) capabilities. It bodes well for FMGs, whose medical background and clinical expertise offer them an advantage in the employment market for drug safety and healthcare informatics.
If you want to assist patients without providing direct care, a career in Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance could be the right choice. It provides numerous work alternatives at every career stage, thanks to faster-than-average employment growth and job opportunities in a variety of disciplines.
Career opportunities in the drug safety sector tend to be prevalent in large organizations. As a result, drug safety jobs are handy for aspiring candidates. Through our Advanced Drug Safety Internship Program, you gain the knowledge you need, and the practical experience employers in this field are demanding.