May 12, 2025
Published by Sollers college at May 12, 2025
Introduction The U.S. healthcare and pharmaceutical industries are rapidly expanding, particularly in clinical research. This surge presents an incredible opportunity for International Medical […]
April 28, 2025
Published by Sollers college at April 28, 2025
Introduction The U.S. healthcare system is undergoing a data and innovation-driven transformation—and at the heart of this revolution is Clinical Trial Management (CTM). […]
May 29, 2024
Published by Sollers college at May 29, 2024
Medical professionals are essential to drug testing, helping from the very beginning to the point of approval. Their participation guarantees clinical trials‘ efficacy, […]
May 16, 2024
Published by Sollers college at May 16, 2024
An autonomous clinical trial: what is it? The terms virtual, home, remote, and siteless are some of the terms used to characterize the […]
May 7, 2024
Published by Sollers college at May 7, 2024
By 2024, adaptive AI is expected to continue gaining popularity worldwide and be swiftly embraced by additional sectors of the economy. However, despite […]
April 30, 2024
Published by Sollers college at April 30, 2024
The rush to create a vaccine has brought attention to the process of bringing a medication to market like never before, making it […]
April 25, 2024
Published by Sollers college at April 25, 2024
Pharmacovigilance is the research and practices associated with the identification, evaluation, comprehension, and avoidance of side effects and other medication-related issues. As it […]
April 10, 2024
Published by Sollers college at April 10, 2024
Clinical trial efficiency may be enhanced by artificial intelligence (AI) enabled systems that enhance patient and location acquisition. Three Strategies Artificial Intelligence Can […]
March 22, 2022
Published by Sollers college at March 22, 2022
CRAs who wish to advance their careers might wonder where to begin if they have some experience in clinical research. There may be […]
November 8, 2021
Published by Sollers college at November 8, 2021
Almost all of the time, the healthcare business is under pressure to achieve greater results than previously. Doctors, nurses, workers, and others must […]
October 21, 2021
Published by Sollers college at October 21, 2021
A Complete Overview of CTMS Software The Clinical Trial Management System is a suite of tools for planning, managing, and tracking clinical studies. […]
October 12, 2021
Published by Sollers college at October 12, 2021
As clinical research experts, the importance of patient-donated data. Clinical trials may be time-consuming and even burdensome for patients, many organizations are trying […]
August 26, 2021
Published by Sollers college at August 26, 2021
Clinical research has grown to be one of the primary components these days. It is a notable field of study which assists in […]
July 21, 2021
Published by Sollers college at July 21, 2021
Clinical trials are necessary for medical research. Producing new medicines to the market depends on the strength of research organizations and drug companies […]
March 4, 2021
Published by Sollers college at March 4, 2021
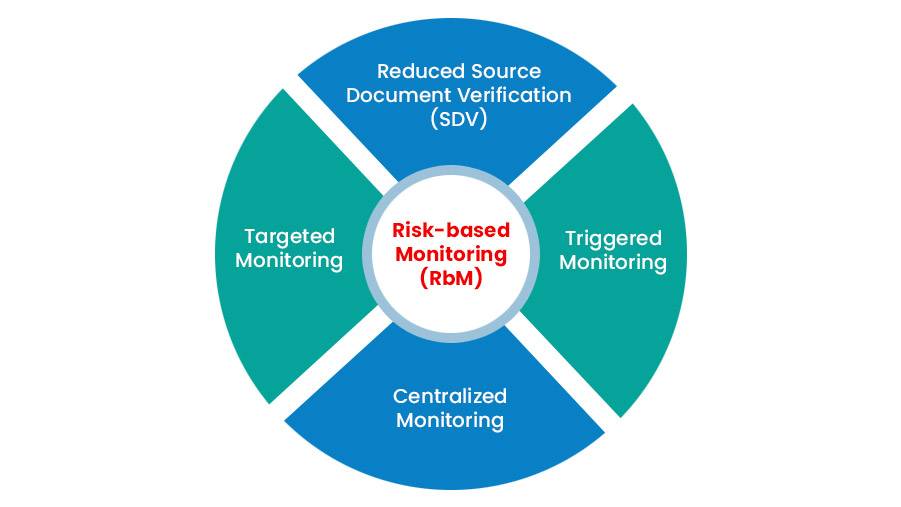
The complexity and cost of clinical trials have increased dramatically in recent years.With rapid advancements in Clinical trials, the methodologies used to support […]