The term “aggregate” means a compilation or collection of different elements or factors. Therefore, the aggregate reporting definition is a report of the aggregate factors affecting the safety and efficacy of a product.
Largely performed on drugs and medications as a part of pharmacovigilance, aggregate reporting is performed on the product before it is commercialized (pre-marketing) and after it is sent into the market (post-marketing).
This article explains what is an aggregate report and its importance, criteria, and challenges along with the role of aggregate reports in pharmacovigilance.
What is an Aggregate Report?
Every product made for public use goes through stages of research and development (R&D), clinical trials, and manufacturing before being marketed for widespread utilization. Even once in the market, the safety, benefits, and risks of the product are monitored for its continued safe use. This evaluation and monitoring of the product’s safety is done through aggregate reports.
Aggregate reporting involves compiling information and observations throughout the life cycle of a product and reporting it to the concerned national regulatory authorities. These reports are timely and constant, used to evaluate the benefits and risks of the product. These reports can be categorized into two phases, namely pre-marketing aggregate reports and post-marketing aggregate reports.
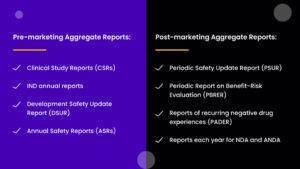
Pre-marketing Aggregate Reports
This phase of aggregate reporting compiles information from the research and development of the product to its final clinical trials and manufacture. Pre-marketing aggregate reports include the following:
1. Clinical Study Reports (CSRs)
These reports include data from multiple clinical trials to assess the risks and efficacy of the test drug.
2. IND Annual Reports
These reports summarize the progress of ongoing clinical trials to inform the regulatory authorities of the safety data and any significant information. Performed under an Investigational New Drug (IND) application, this report ensures that the product continues to stand by the regulatory standards.
3. Development Safety Update Reports (DSURs)
These reports involve an annual review of the data collected on the safety of the drug during its clinical trials.
4. Annual Safety Reports (ASRs)
These reports are also annual accounts of clinical trials of the drugs. ASRs, however, focus mostly on the adverse events observed during the trials and the overall safety findings.
Post-marketing Aggregate Reports
This phase of aggregate reporting is concerned with the benefits and adverse effects observed by the public on taking the drug. These reports do not focus on individual cases but on the overall estimates of a region. Post-marketing aggregate reports offer more extensive and detailed information on the benefits and risks of a drug than could be determined through clinical trials. This reporting phase includes the following:
1. Periodic Safety Update Reports (PSURs)
These are the reports regarding the drug’s safety profile submitted periodically to the regulatory bodies after the drug is marketed. PSURs evaluate any new safety information and, based on that, reassess the benefit-risk balance of the drug to ensure the safety of its continued use.
2. Periodic Reports on Benefit-Risk Evaluation
These reports involve regular assessments of the overall benefit-risk profile of a drug after it is marketed for public use. It uses new data on the efficacy and safety of the drug to update and reevaluate the pre-existing data.
3. Reports of Recurring Negative Drug Experiences (PADER)
These reports document any repeated adverse reactions noted on the use of the drug. It also includes characteristic symptoms that may raise safety concerns associated with this drug.
4. Reports Each Year for NDA and ANDA
This includes sending annual reports to New Drug Applications (NDA) and Abbreviated New Drug Applications (ANDA). These reports include a summary of all significant information regarding any changes in the manufacturing, labeling, and clinical trial data of the drug in the previous year.
Aggregate Reports in Pharmacovigilance
Pharmacovigilance is the science that deals with the activities related to the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of adverse drug reactions (ADRs). It follows a systematic approach to monitoring and improving the safe use of medicines.
The drug safety aggregate reports in pharmacovigilance are presented to regulators as soon as the medicine is marketed all-around and facilitate understanding of the product’s risk and benefit profile over time. These reports focus not on individual cases, but preferably on an overview, assessment of the safety profile, and benefit-risk-evaluation of Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) and Serious Adverse Event (SAE) and pregnancy reports.
Importance of Aggregate Reporting
Every drug goes through several levels of clinical trials before being allowed to be marketed. However, detailed analysis and evaluation of a drug’s benefit-to-risk ratio are not possible at this level of trial. Real-world drug safety data must be gathered in the post-marketing phase because more people are exposed to the drugs in the real world than in clinical trials. Therefore, periodically reviewing safety reports received cumulatively worldwide becomes highly significant to analyze the product’s benefit and risk balance.
Aggregate reporting of a drug is important for the following reasons:
- Rare AEs (adverse events) that have not yet been recognized may become apparent at the post-marketing stage.
- Patients with underlying diseases who receive medications in real life frequently experience a variety of side effects. Such information will be essential for further research to determine the product’s limitations when provided through aggregate reports.
- The post-marketing studies carried out to show drug efficacy and risk stratification can reveal deviations in the benefit-risk balance of pharmaceuticals.
- It is imperative to identify and report new and evolving information on risks and evidence of benefits, all of which are amply reflected in aggregate reports.
Challenges in Aggregate Reporting
Compiling aggregate reports and submitting them legally can be challenging due to the nature of the process. Due to the wide variety of reports that must be included in the submission, the documentation process is frequently quite difficult. While the process largely uses electronic means now, aggregate reporting is still a labor-intensive manual process.
Some challenges involved in preparing and maintaining aggregate reports are:
- There must be consistency in any report updates.
- The regulatory team, the safety and clinical team, and the marketing team, among others, must provide timely updates on information from various stakeholders.
- Each report must be tracked from submission to approval by pharmaceutical companies.
- They must also recognize and check the line listings for accuracy, considering the variety of data involved.
- The reporting process involves enormous amounts of data, and those amounts keep growing every day.
- The risks of errors leading to non-compliance findings are a major source of worry for the pharmaceutical industry.
- The regulatory guidelines are periodically revised in stages and are not consistent worldwide, necessitating the use of multiple trackers for various products and nations.
Learn Aggregate Reporting at Sollers College
Sollers provides a short-term program for Aggregate Reporting and a certificate program for graduates in the Advanced Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance Program. These unique programs were developed for professionals who want to work in the field of drug safety and are based on the popular, business-based Oracle Argus Safety Database Software.
Pharmacovigilance is currently the focus of the healthcare industry to balance risks and benefits. The Aggregate Reporting and the Advanced Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance programs at Sollers College encompass a curriculum that is in line with the needs of the market, is very competent, and prepares professionals for a career in the pharmaceutical sector. These programs were created to satisfy the requirements of this heavily regulated and ever-expanding industry.